The Microsoft Text Input application, also known as TextInputHost.exe, is a mysterious system process that can plague Windows 10 users with high CPU usage. If you’re having trouble with this process, you’ve come to the right place.
In this tutorial, we’ll explain everything you need to know about the Microsoft Text Input application, including what it is, what it does, and how to reduce its CPU usage.
What Is the Microsoft Text Input Application?
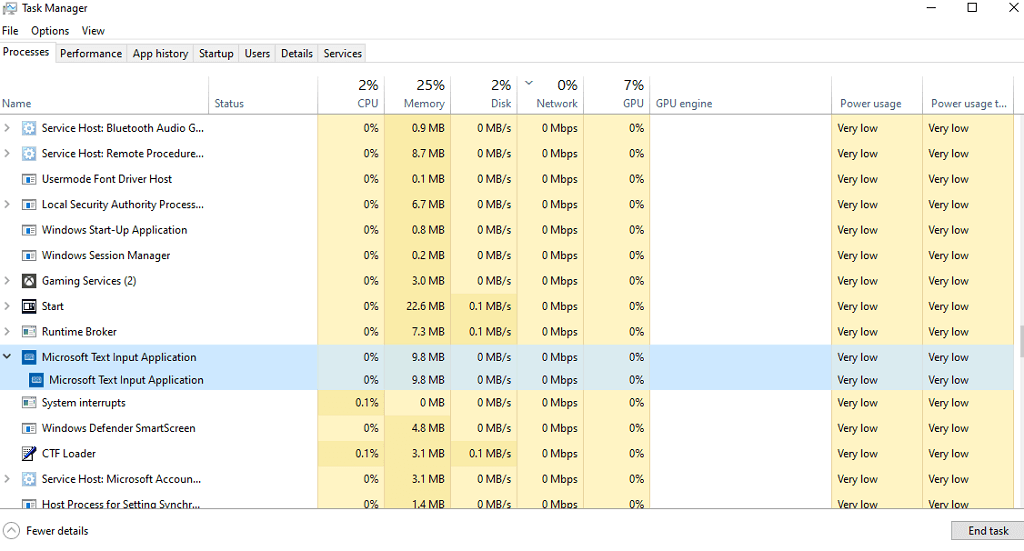
The Microsoft Text Input application is a system executable file that enables the text input process and various other features such as touch keyboard functionality. It can appear as TextInputHost.exe, InputApp.exe, or Windows System File in the Task Manager.
Some of its key functions include enabling the Emoji Keyboard, advanced screenshots, and the Multi-Clipboard.
Is the Microsoft Text Input Application Safe?
The Microsoft Text Input Application is a legitimate Windows process. However, it can start to cause system crashes, affecting the performance of your PC by using up too much of the CPU’s resources. This seems to most commonly occur in Build 1903 of Windows 10.
Because of this, many users flag it as potentially being malicious software like malware, a keylogger, or a cryptocurrency miner. While this is possible in some cases, it’s highly unlikely.
To ensure that your Microsoft Text Input Application is the legitimate version, you can check whether it’s certified under Microsoft Digital Ownership:
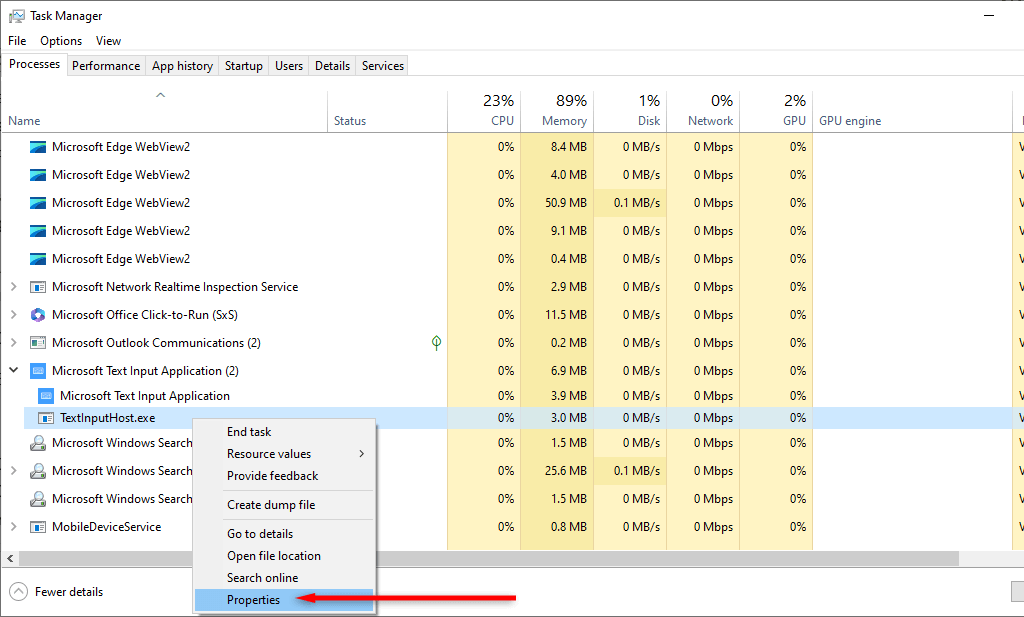
- Open the Task Manager then right-click the TextInputHost.exe process.
- Select Properties.
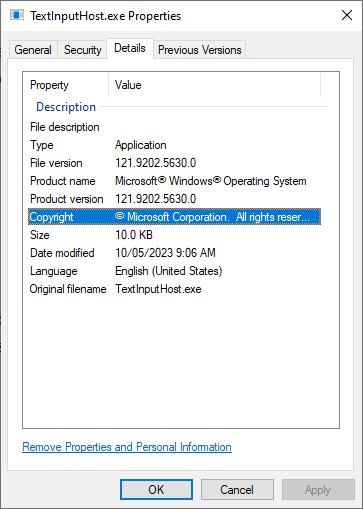
- Choose the Details tab and make sure that the Product Name is “Microsoft Windows Operating System” and the Copyright says “Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.” You can double-check this by choosing the Digital Signatures tab and making sure that the Name of signer is Microsoft Windows.
You can also verify that TextInputHost.exe is authentic by checking its location in your system. It should be found in either:
- C:\Windows\SystemApps\MicrosoftWindows.Client.CBS_cw5n1h2txyewy, or;
- C:\Windows\SystemApps\MicrosoftWindows.Client.CBS_cw5n1h2txyewy/InputApp.
If you can’t verify the authenticity of the process, you should run your antivirus software immediately.
Can I Disable the Microsoft Text Input Application?
Yes, it’s safe to disable the Microsoft Text Input Application. However, it may cause some features to do with on-screen keyboards (and inking and typing personalization) to be disabled, too.
How to Disable the Microsoft Text Input Application Process
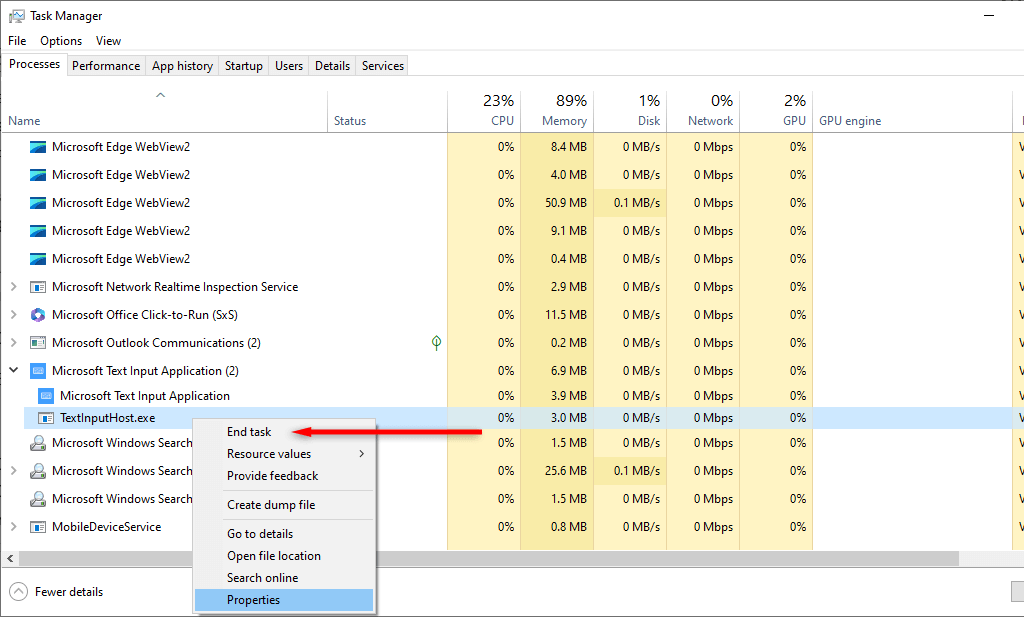
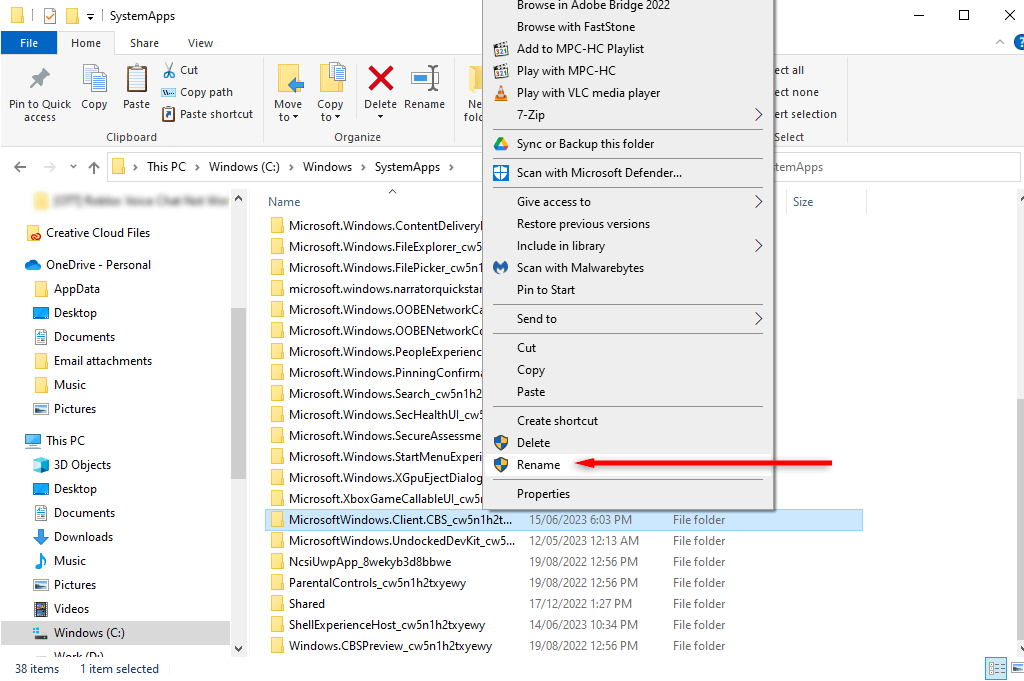
Unfortunately, disabling this system process isn’t as simple as ending the task in Task Manager, since it will reboot on your next startup. Instead, the easiest way to disable the MS Text Input Application is by renaming its root folder. This prevents Windows from locating and rebooting the app.
To disable the Microsoft Text Input Application process:
- Right-click the Start Menu and select Task Manager from the pop-up menu.
- Select the Processes tab.
- Right-click the process and select Properties.
- Select the General tab, and note the file location. It’s usually located at
C:\Windows\SystemApps\MicrosoftWindows.Client.CBS_cw5n1h2txyewy, but this may vary depending on your Windows version (including whether you’re using Windows 10 or Windows 11). - Right-click the Microsoft Text Input Application and select End Task.
- Now, press the Win key + E to open File Explorer and navigate to the folder above. Alternatively, right-click the process in Task Manager and select Open file location.
- Rename the root folder. The best way is to add a letter or number in front of the existing name so that it’s easy to revert in case you ever need to.
Note: This may only be a temporary fix, depending on future Windows updates. When you perform a system update, Windows might automatically rename or reinstall the folder, meaning you’ll have to perform these steps again. It isn’t possible to permanently uninstall the process.
Improve Your PC’s Performance
Things occasionally go wrong with Microsoft’s essential processes, causing increased system usage, crashes, and other problems. But hopefully, with this guide, you’re able to get your PC running normally once again.