Pros and cons, different usage scenarios
When running an Ethernet cable from your router to your PC isn’t an option, you’re left picking between the lesser of two evils – WiFi extenders or powerline adapters. But which of these is the best?
Both technologies have their pros and cons and we’ll be looking at both to explain how each option may be suitable for you. Ultimately though, it’ll come down to your specific usage scenario. More on determining that below.
WiFi Extenders and Powerline Adapters – What’s the Difference?
WiFi extenders and powerline adapters are two very different types of technology that are both designed to achieve the same goal – provide a more reliable Internet connection over a longer distance.
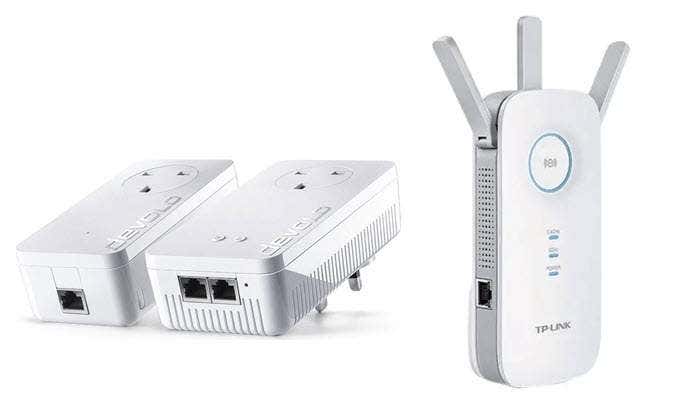
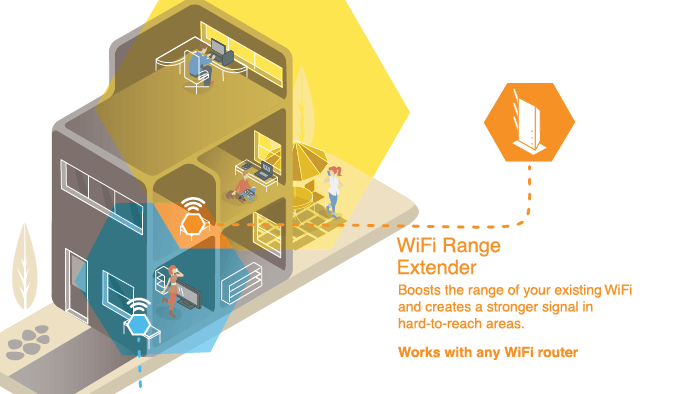
A WiFi extender is essentially like a small hub that can physically be placed in between both your router and your PC to take the WiFi signal from your router and extend it out to a longer distance.
A powerline adapter requires two outlets, plugged into the mains of your home. The powerline adapters can connect wirelessly or wired to your router and send the network data through the electric wiring of your home, which allows it to travel further and remove the restriction of walls.
Which is Better? A Powerline Adapter or WiFi Extender?
Now that we’ve briefly explained the technology behind powerline adapters and WiFi extenders, let’s take a look at the performance of both. Obviously, the goal for both products is to allow a computer to get a stronger signal, usually because the WiFi signal from the router is out of range.
While a WiFi extender can extend the WiFi signal, there is significant degradation when you use such a product. This is because the signal is beamed to one location, then beamed to another. This can add to the latency of your network and lower your overall speeds. Through all of this, walls, furniture, or ceilings can still get in the way of your signal, too.
Powerline adapters, on the other hand, simply convert the network data from your router and carry it directly to your PC through electrical wiring. As far as latency is concerned, powerline adapters are far superior to WiFi extenders.
The speeds you’ll get using a powerline adapter are dependent on the quality of your home’s electric wiring. This means that while a powerline adapter can generally be the most suitable solution to boosting your network range, it isn’t suitable for everybody.
For example, my own home’s wiring is good enough that I can get very close to my network’s full speeds, and in turn very close to the speed an Ethernet cable would give. As a result, I’d recommend purchasing a powerline adapter first and if you get slow speeds, return it and try a WiFi extender instead.
How to Install a Powerline Adapter – Top Tips
Because powerline adapters run network data through the electrical wiring in your home, many people are scared away from the technology. The common belief is that they are hard to set up and require DIY skills. Fortunately, this isn’t true at all and powerline adapters are very easy to set up.
The overall process may differ from brand to brand, but generally all you need to do is plug in your powerline adapters into two empty wall sockets, connect them to your network, and press the Pair buttons. Some of the newer ones will auto-detect each other, making the setup process even easier.
For example, my TP-Link AV600 mbps Nano Powerline adapter has the following instructions.
To create a secure powerline network:
- Plug in the two powerline adapters into wall sockets.
- Press the pair button on one adapter.
- Press the pair button on another adapter.
The great thing about powerline adapters is that you can add many to the same network. This allows you to get great Internet connection in all rooms, without trailing Ethernet cables around. As seen below, the instructions are very similar for adding new adapters to an existing network.
To join an existing powerline network:
- Press the pair button on any adapter in the existing network.
- Press the pair button on the new adapter.
We’d highly recommend purchasing a powerline adapter that includes an Ethernet cable. This will allow you to connect the adapters directly to your router and directly to your PC, reducing latency and the risk of potential packet loss or connection drop outs.
Can a Powerline Adapter Beat Ethernet Cable?
Even if you have excellent electrical wiring in your home, a powerline adapter can never be as reliable as an Ethernet cable. A powerline adapter lets network travel through electric wiring and it’s a physical connection between your PC and your router, but it’s still not as reliable as a direct Ethernet connection from your router to your PC.
Granted, using a WiFi connection can never be 100% reliable either – you can receive dropouts due to interference from other wireless signals or when furniture or walls interfere with the signal. Powerline adapters reduce the interference caused significantly, but never completely.
Much like a typical WiFi router, another thing to consider is that powerline adapters can drop in performance if they overheat. An Ethernet cable, on the other hand, will never have this problem.
In most cases, a powerline adapter can reach close to or the same speeds as an Ethernet connection in optimal conditions, but you may still experience the occasional drop in latency or connection. If you need to rely on crystal clear connection with minimum dropouts, you absolutely must use an Ethernet cable.
Summary
To summarize this topic, a powerline adapter is almost always the best option. In rare cases, your own home’s electrical wiring may not be optimal, which will mean a WiFi extender would be more suitable.
In all cases, an Ethernet cable is still the most suitable option. You can find Ethernet cables that are 100 feet in length or more on Amazon, so you should never have issue with distance. Enjoy!