We show you its benefits as well as disadvantages
These days just about every part of our digital lives involves some form of credentials for authentication. It’s enough to make it virtually impossible to manage them yourself.
While third-party solutions abound, Microsoft Windows has its own built-in credentials manager, but just what can it do?
How Windows Credential Manager Works
Windows Credential Manager is a built-in Windows feature that allows users to securely store and manage their login credentials for various network resources, websites, and applications.
It’s available in the following versions of Windows:
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 8
- Windows 7
- Windows Vista
It acts as a central repository for storing and managing these generic credentials, allowing users to easily log in to their user accounts without having to remember and enter their username and password every time.
When a user logs in to a network resource, website, or apps for the first time, Windows Credential Manager prompts them to save their login credentials. If users save their credentials, they will be securely stored in the Windows Credential Manager vault.
When the user attempts to access the same network resource, website, or application again, Windows Credential Manager automatically retrieves their saved credentials and logs them in automatically, without the user having to enter their username and password again.
Windows Credential Manager also allows users to manage their stored credentials and update, backup, or delete them as needed. This can be done through the Windows Control Panel or by using the command line interface.
Benefits of Using Windows Credential Manager
There are several benefits to using Windows Credential Manager, including:
- It saves time and effort by automatically filling in login credentials for network resources, websites, and applications that the user has previously logged in to. This eliminates the need for the user to remember and manually enter their username and password.
- It improves security by securely storing login credentials in an encrypted vault, protecting them from unauthorized access. This reduces the risk of password-related security breaches, such as password cracking or phishing attacks.
- It allows users to manage and update their stored login credentials easily. Users can also back up and restore credentials.
- It integrates seamlessly with Windows, making it a convenient and reliable option for managing login credentials on a Windows computer.
Windows credentials manager may not be as elaborate or feature-rich as third-party alternatives such as LastPass or 1Password. Still, it’s free, pre-installed, and designed to be part of the operating system.
How to Access and Manage Credentials in Windows Credential Manager
To access and manage credentials in Windows Credential Manager, follow these steps:
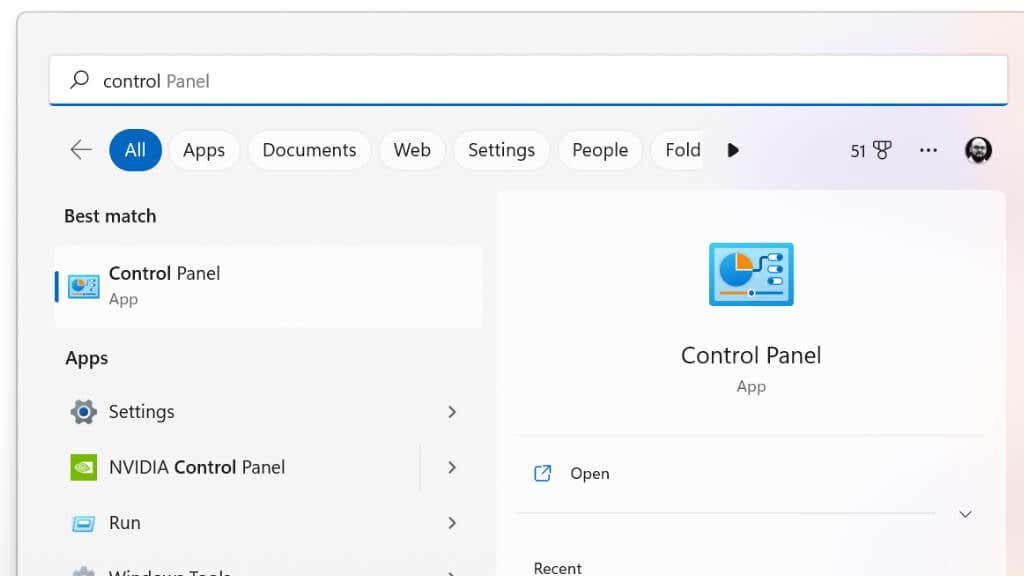
- Open the Windows Control Panel by searching for it in the Start Menu.
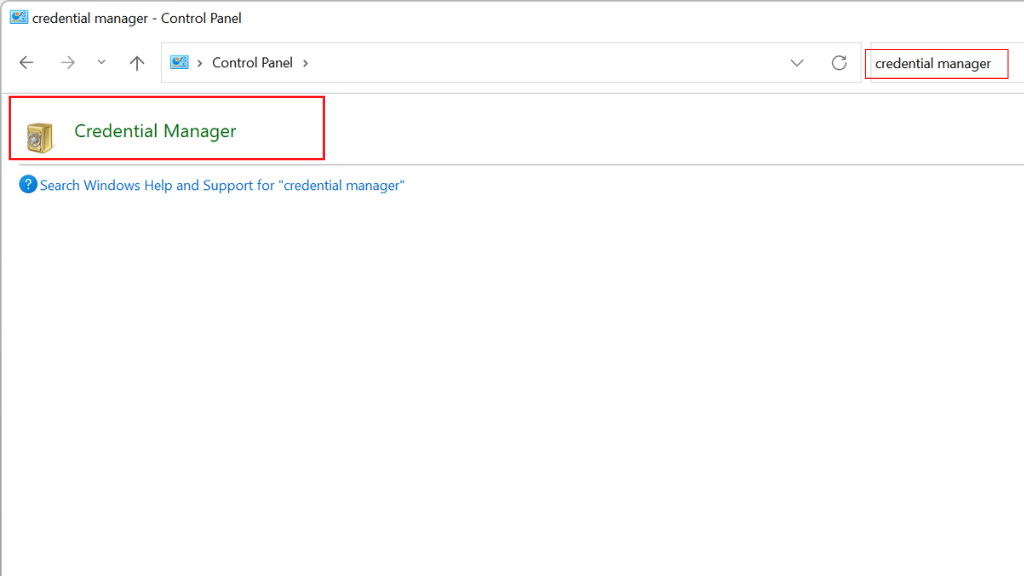
- In the search box, type credential manager and select it from the search results.
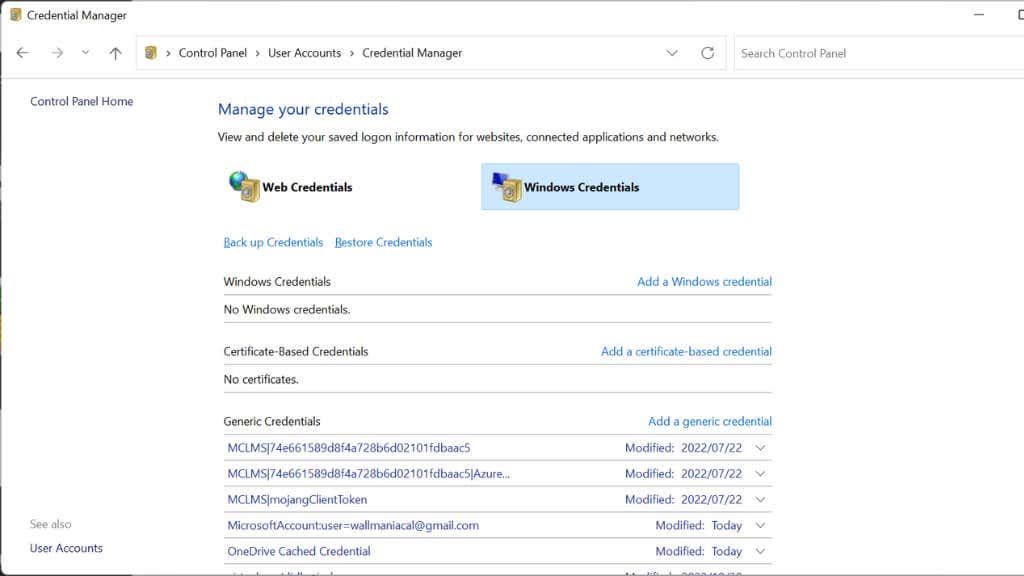
- In the Credential Manager window, select the Web Credentials or Windows Credentials tab, depending on the type of credentials you want to manage.
- To view the details of a specific credential, select it from the list and click the Dropdown arrow.
- To update a credential, select it from the list and click the Edit button. Make the necessary changes and click OK to save them.
- To delete a credential, select it from the list and click the Remove button. Confirm that you want to delete the credential by clicking Yes in the confirmation window.
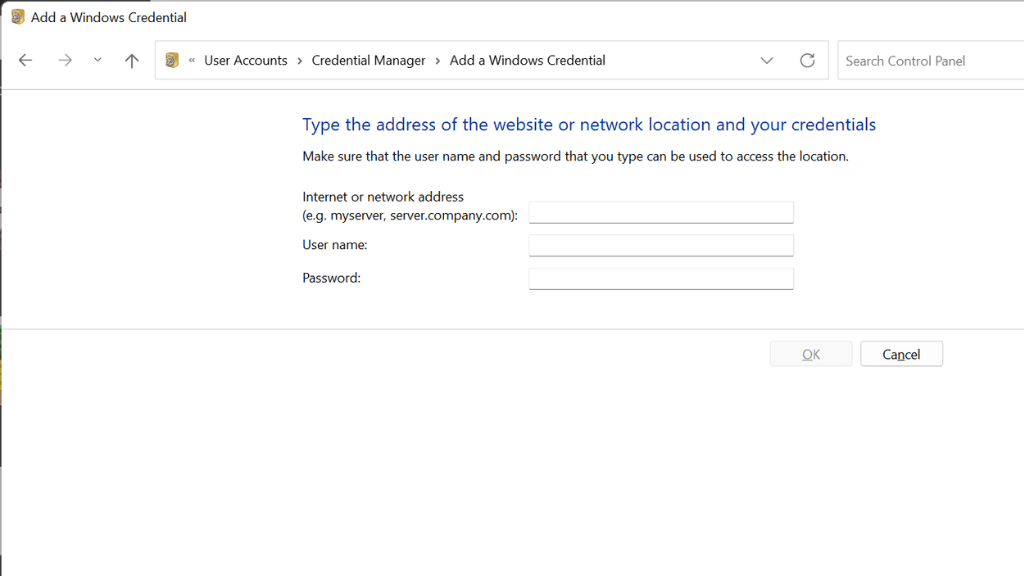
- To add a credential, select the type of credential you want to add, and then enter the details.
Alternatively, you can manage credentials in Windows Credential Manager using the command line interface. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the command prompt by typing cmd in the search box and selecting Command Prompt from the search results.
- Type the following command to view the list of stored credentials: cmdkey /list
- To view the details of a specific credential, use the following command, replacing “CREDENTIAL_NAME” with the name of the credential you want to view:
cmdkey /v CREDENTIAL_NAME
- To add or update a credential, use the following command, replacing “CREDENTIAL_NAME” and “USERNAME” with the appropriate values:
cmdkey /add:CREDENTIAL_NAME /user:USERNAME /pass:PASSWORD
- To delete a credential, use the following command, replacing “CREDENTIAL_NAME” with the name of the credential you want to delete:
cmdkey /delete:CREDENTIAL_NAME
The command line method is hardly ever necessary, but it’s nice to have the option!
Troubleshooting Common Issues With Windows Credential Manager
Credential Manager can be useful for storing login information for websites, network resources, and other services that you access on a regular basis. However, like any other tool, Credential Manager can sometimes encounter issues and may not work as expected.
These are some common issues you may encounter with some possible solutions:
- Credential Manager is not saving your login information: This could be due to a problem with the service itself. Try restarting the service by going to the Start menu and typing services.msc into the search box and press Enter. Locate the Credential Manager service, right-click on it and select Restart.
- Credential Manager is not showing your login information: This could be due to a problem with the stored credentials. Try deleting the existing credentials and re-entering them to see if that fixes the issue. To do this, open Credential Manager, select the credentials that you want to delete, and click on the Remove button. Then, re-enter the credentials and save them. Of course, copy and paste them somewhere safe first!
- Credential Manager is not working: This could be due to a problem with the service itself or with the operating system. Try restarting your computer and see if that fixes the issue. If the problem persists, you may need to update Windows.
Since Credential Manager is an integral part of Windows, it can actually be harder to troubleshoot than a third-party solution. Luckily serious issues seem to be rare and the above fixes are usually enough.
How to Back Up Credentials
It’s great that Credential Manager keeps all your credentials safe and encrypted, but what if something happens to your computer? To back up your passwords with Windows Credential Manager, follow these steps:
- Open Credential Manager by going to the Start menu and typing credential manager into the search box.
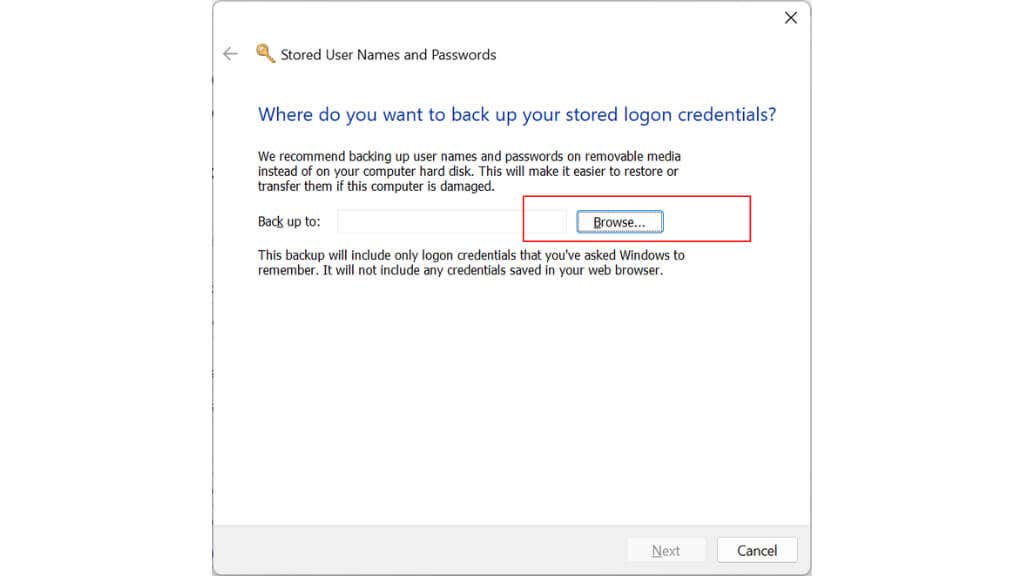
- Click on the Back up credentials to export the selected credentials to a file.
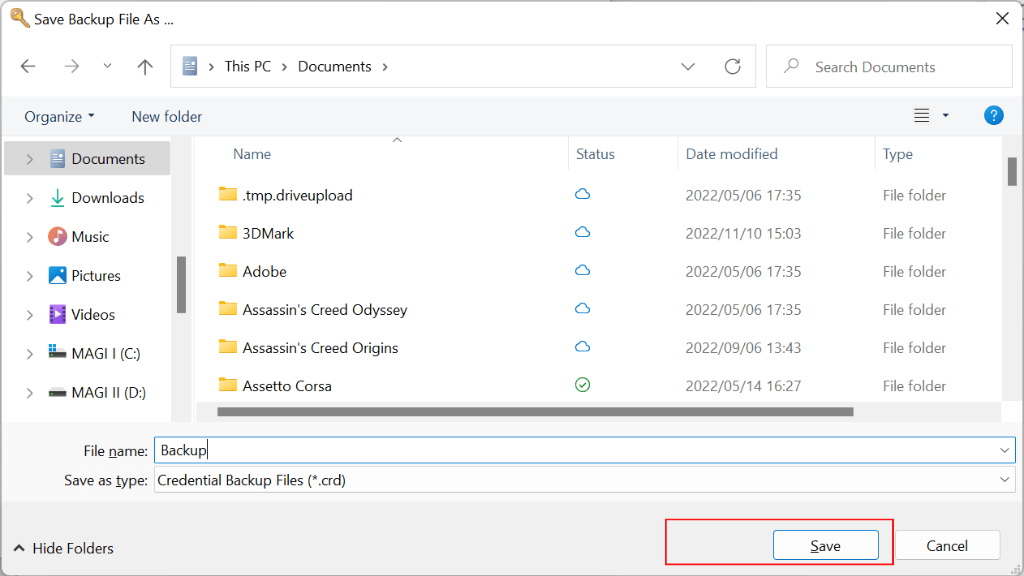
- Choose a location to save the file and give it a name.
- Click on the Save button to save the file.
- You can then use this file to restore your credentials if they are lost or deleted.
The exported backup file will be in a special format that can only be read by Credential Manager, so you cannot open it with a text editor or other program. It is also a good idea to keep the file in a safe and secure location, such as an external hard drive or cloud storage service, in case your computer is lost or damaged.
Certificate-Based Credentials
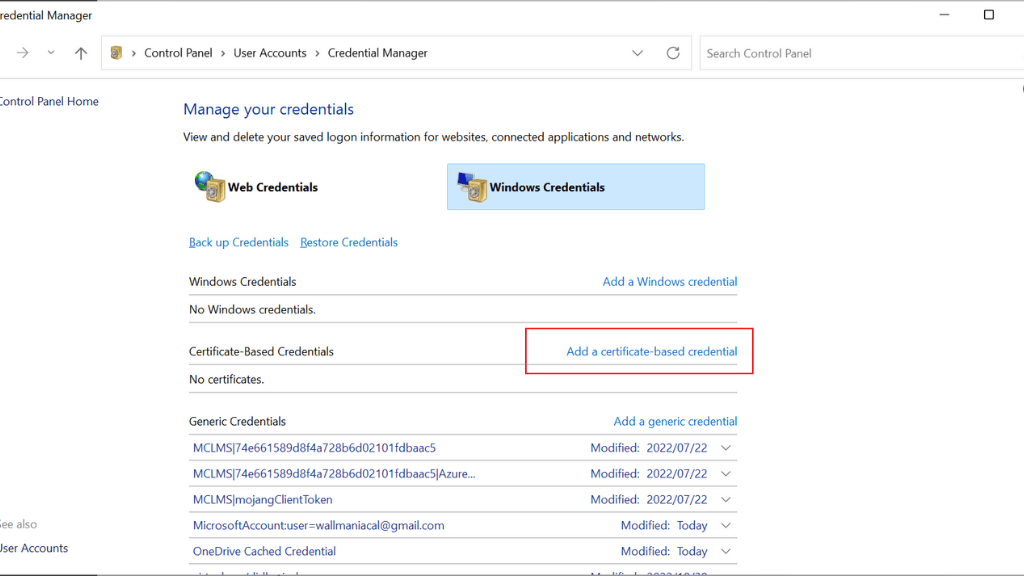
Credential Manager can be used to store and manage certificate-based credentials, which are digital certificates that are used to authenticate your identity and grant you access to certain resources or services.
To use certificate-based credentials with Credential Manager, you will need to install the certificate on your computer and then add it to Credential Manager using Add a certificate-based credential under Windows Credentials.
Generating Strong Passwords
The Windows Credential Manager does not include a password generation feature. It is primarily used to store and manage login credentials for various websites and applications.
This means you’ll have to rely on your web browser of choice, which virtually all both have strong password generators and managers. That includes Microsoft Edge (which replaces Internet Explorer), which is also included with Windows, so you don’t have to download anything extra to generate passwords.
If you want to be more involved with making secure passwords of your own, have a look at 3 Ways To Come Up With the Most Secure Password.
Alternatives to Windows Credential Manager
If you are looking for an alternative to Windows Credential Manager, there are several options available, both free and paid. Some popular alternatives include:
- LastPass: LastPass is a free password manager that can store your login information and automatically fill in forms for you. It also has a feature called “Security Challenge” that can help you identify and fix weak passwords.
- 1Password: 1Password is a paid password manager that offers features such as password generation, password sharing, and password auditing. It also has a built-in password manager for your browser.
- KeePass: KeePass is a free and open-source password manager that can store your login information and automatically fill in forms for you. It also has features such as password generation, password sharing, and password auditing.
- Dashlane: Dashlane is a paid password manager that offers features such as password generation, password sharing, and password auditing. It also has a built-in password manager for your browser.
- RoboForm: RoboForm is a paid password manager that offers features such as password generation, password sharing, and password auditing. It also has a built-in password manager for your browser.
There are many more alternatives to Windows Credential Manager that offer similar or additional features. It may be worth considering switching to a different password manager if you are experiencing issues with Credential Manager or if you want more advanced features.
This is especially true, since with Windows Credential Manager, anyone with admin access to your computer can see your credentials. This is a vulnerability not shared by third-party managers, and should be a primary consideration when choosing where to store your passwords.